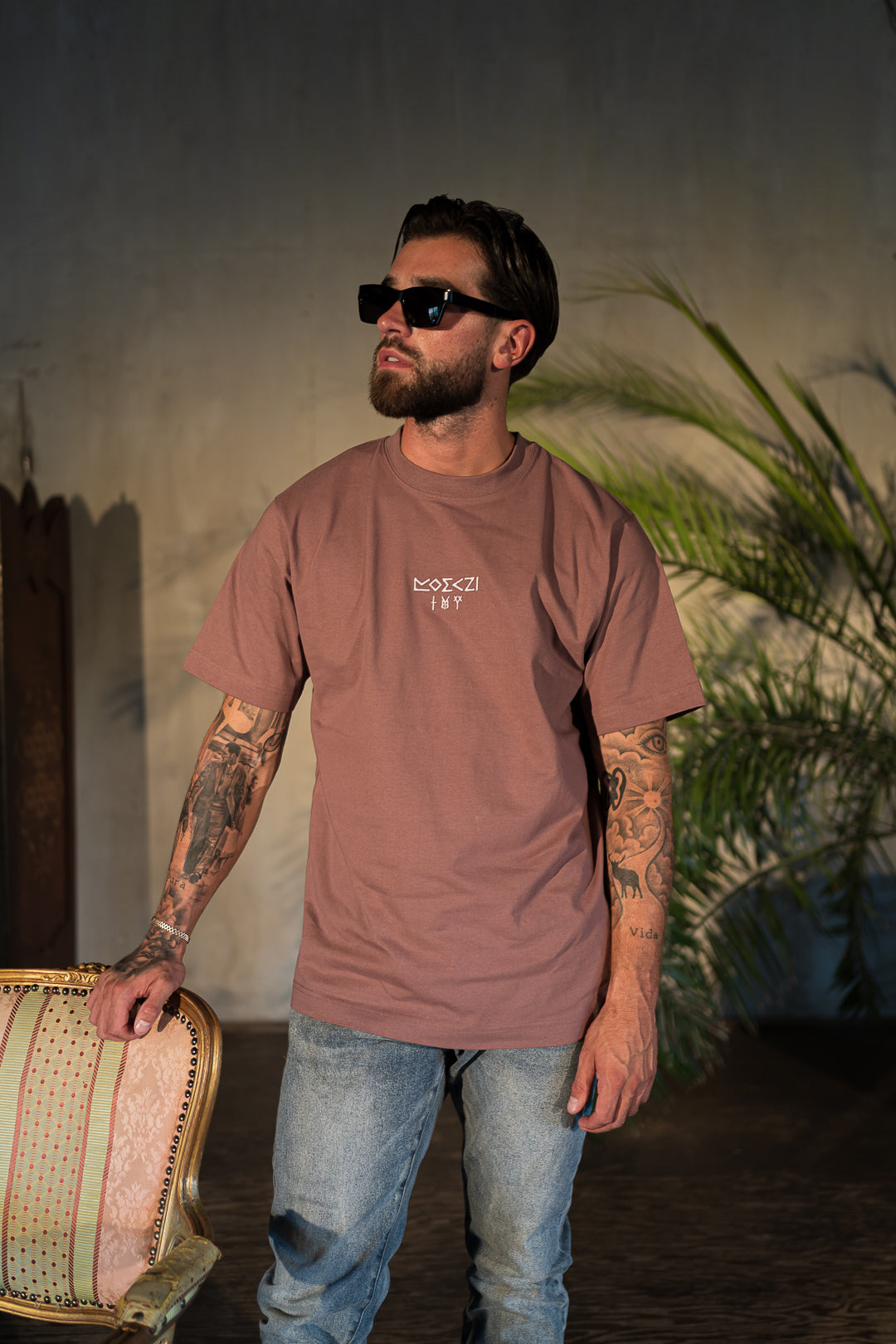
Ancient Greece
The story of Archaia
The Linear B alphabet is a remarkable treasure that offers us a glimpse into ancient Greece. This ancient writing system, dating back to the late Bronze Age, is considered one of the earliest written forms of Greek. It is named after the linear forms of the characters used to express the language.
The discovery of the Linear B alphabet in the early 20th century sparked excitement among archaeologists and linguists. It was first deciphered by the English architect Michael Ventris in 1952, resulting in a better understanding of the Minoan and Mycenaean civilizations that once thrived in the Aegean region.
The Linear B alphabet consists of more than 80 characters, each with a specific phonetic value. The script was primarily used for administrative and accounting purposes, with clay tablets being used to record information such as inventories, contracts, and lists of goods and services.
Thanks to the Linear B alphabet, historians have gained important insights into the economy, politics, and social structures of ancient Greek civilizations. It has helped us understand trade practices, religious customs, and even the names of rulers and gods of that time.

The story behind the Archaia Piece
Although overshadowed by the later Greek alphabet, the Linear B alphabet has had a lasting impact on our understanding of the ancient world. It reminds us that written language is not just a means of communication but also a window into the past.
Today, we can still marvel at the fascination of the Linear B alphabet. It offers us the opportunity to feel a connection with people who wrote the same characters thousands of years ago. It is a reminder of the richness and complexity of our human history and the eternal quest for knowledge.
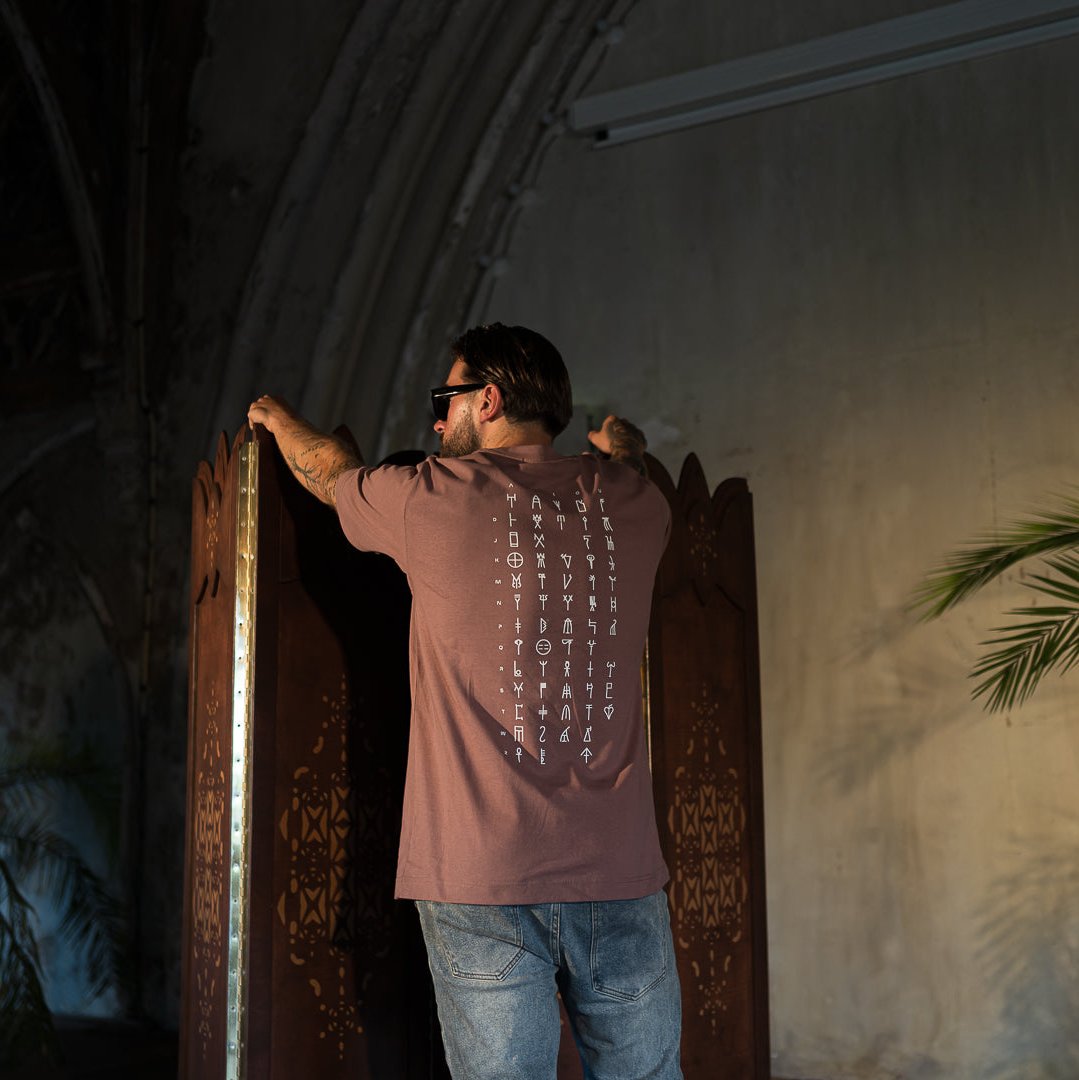
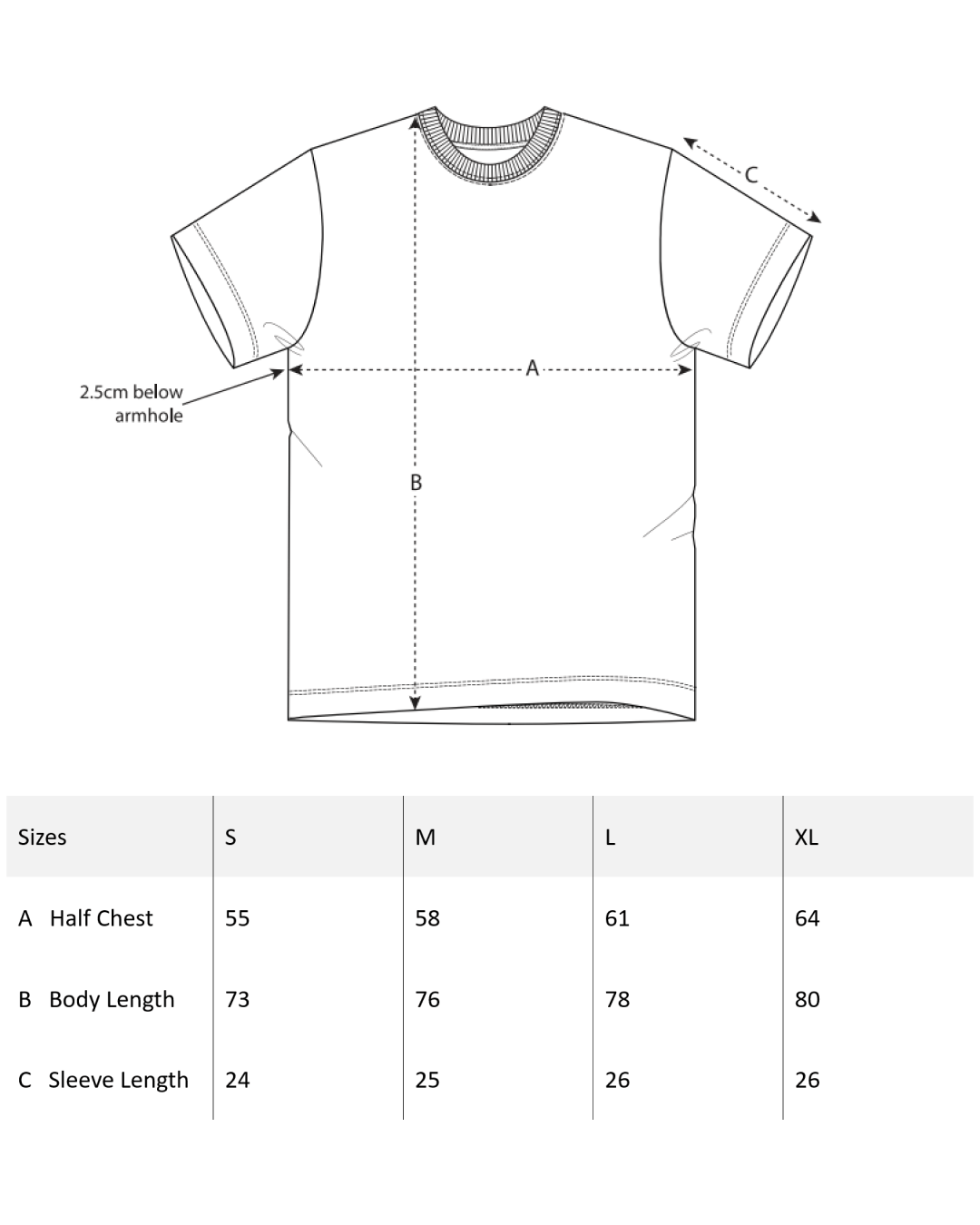
While there are still special characters and undeciphered symbols, the back of the Archaia T-shirt features a syllable chart. Each syllable begins with a consonant and is combined with a vowel (above), except for tge top row. The chart can be read as follows: a, e, i, o, u, da, de, di, do, du.. and so on.
Cultural Piece
Archaia (ἀρχαία)